驱动结构
结构如图:
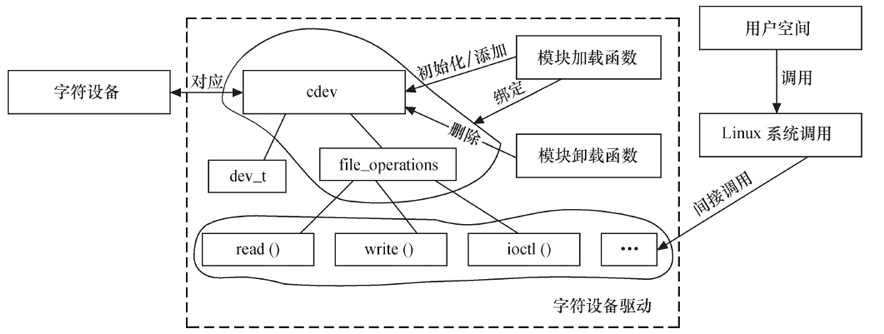
cdev结构体
在Linux内核中,cdev结构体是表示字符设备的结构体之一。字符设备是一种特殊类型的设备,它以字符为单位进行输入和输出,例如终端、串口等。
cdev结构体用于表示字符设备,它包含了所有与该设备相关的信息和属性。cdev结构体定义在头文件<linux/cdev.h>中,其定义如下:
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj;
struct module *owner;
const struct file_operations *ops;
struct list_head list;
dev_t dev;
unsigned int count;
};
cdev结构体中的重要成员变量包括:
-
kobj:一个kobject结构体,用于表示cdev对象在内核中的位置。
-
owner:该cdev对象所属的模块。
-
ops:一个file_operations结构体指针,其中包含该设备支持的所有文件操作函数。
-
list:一个list_head结构体,用于将该cdev对象连接到设备列表中。
-
dev:该字符设备的设备号。
-
count:该字符设备的数量。
dev_t成员
cdev结构体的dev_t成员定义了设备号,为32位,其中12位为主设备号,20位为次设备号。使用下列宏可以从dev_t获得主设备号和次设备号:
#define MINORBITS 20
#define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1)
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS))
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK))
而使用下列宏则可以通过主设备号和次设备号生成dev_t:
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
cdev操作函数
void cdev_init(struct cdev *, const struct file_operations *);
struct cdev *cdev_alloc(void);
void cdev_put(struct cdev *p);
int cdev_add(struct cdev *, dev_t, unsigned);
void cdev_del(struct cdev *);
void cd_forget(struct inode *);
- cdev_init: 函数用于初始化cdev的成员,并建立cdev和file_operations之间的连接
- cdev_alloc: 函数用于动态申请一个cdev内存
- cdev_add: 用于将cdev结构体添加到系统中, 完成字符设备的注册
- cdev_del: 用于从系统中删除cdev结构体, 完成字符设备的注销
分配和释放设备号函数
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name);
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name);
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count);
在调用cdev_add()函数向系统注册字符设备之前,应首先调用register_chrdev_region()或alloc_chrdev_region()函数向系统申请设备号。register_chrdev_region()函数用于已知起始设备的设备号的情况,而alloc_chrdev_region()用于设备号未知,向系统动态申请未被占用的设备号的情况,函数调用成功之后,会把得到的设备号放入第一个参数dev中。alloc_chrdev_region()相比于register_chrdev_region()的优点在于它会自动避开设备号重复的冲突。相应地,在调用cdev_del()函数从系统注销字符设备之后,unregister_chrdev_region()应该被调用以释放原先申请的设备号。
file_operations结构体
在Linux内核中,file_operations结构体是表示字符设备或块设备文件操作的结构体之一。它包含了一组函数指针,这些函数指针用于处理文件操作事件,例如打开、关闭、读取、写入等。
file_operations结构体定义在头文件<linux/fs.h>中,其定义如下:
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*mremap)(struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **, void **);
long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
loff_t len);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *);
#endif
};
下面我们对file_operations结构体中的主要成员进行分析:
llseek()函数用来修改一个文件的当前读写位置,并将新位置返回,在出错时,这个函数返回一个负值。read()函数用来从设备中读取数据,成功时函数返回读取的字节数,出错时返回一个负值。它与用户空间应用程序中的ssize_t read(int fd,void*buf,size_t count)和size_t fread(void*ptr,size_t size,size_t nmemb,FILE*stream)对应。write()函数向设备发送数据,成功时该函数返回写入的字节数。如果此函数未被实现,当用户进行write()系统调用时,将得到-EINVAL返回值。它与用户空间应用程序中的ssize_t write(int fd,const void*buf,size_t count)和size_t fwrite(const void*ptr,size_t size,size_t nmemb,FILE*stream)对应。read()和write()如果返回0,则暗示end-of-file(EOF)。unlocked_ioctl()提供设备相关控制命令的实现(既不是读操作,也不是写操作),当调用成功时,返回给调用程序一个非负值。它与用户空间应用程序调用的int fcntl(int fd,int cmd,.../*arg*/)和int ioctl(int d,int request,...)对应。compat_ioctl()用于处理旧版本的设备驱动程序中的IO控制命令。它被称为“兼容”的IO控制函数,因为它能够处理早期版本的ioctl命令格式,以确保旧的设备驱动程序能够正确地处理IO控制命令。在早期版本的Linux内核中,ioctl命令格式是由一个32位的命令码和一个void指针类型的参数组成的。但是,在新的Linux内核版本中,ioctl命令格式已经更新为一个ioctl_cmd_t结构体,其中包含了更多的信息,例如命令码、参数的长度和指针等。当旧的设备驱动程序需要处理IO控制命令时,它会使用旧的ioctl命令格式,这时应用程序会调用ioctl系统调用来发送命令。然后,ioctl系统调用会将命令传递给设备驱动程序,设备驱动程序会调用compat_ioctl函数来处理该命令。mmap()函数将设备内存映射到进程的虚拟地址空间中,如果设备驱动未实现此函数,用户进行mmap()系统调用时将获得-ENODEV返回值。这个函数对于帧缓冲等设备特别有意义,帧缓冲被映射到用户空间后,应用程序可以直接访问它而无须在内核和应用间进行内存复制。它与用户空间应用程序中的void*mmap(void*addr,size_t length,int prot,int flags,int fd,off_t offset)函数对应。- 当用户空间调用
LinuxAPI函数open()打开设备文件时,设备驱动的open()函数最终被调用。驱动程序可以不实现这个函数,在这种情况下,设备的打开操作永远成功。 - 与
open()函数对应的是release()函数。 poll()函数一般用于询问设备是否可被非阻塞地立即读写。当询问的条件未触发时,用户空间进行select()和poll()系统调用将引起进程的阻塞。aio_read()和aio_write()函数分别对与文件描述符对应的设备进行异步读、写操作。设备实现这两个函数后,用户空间可以对该设备文件描述符执行SYS_io_setup、SYS_io_submit、SYS_io_getevents、SYS_io_destroy等系统调用进行读写。
驱动组成
驱动模块加载和卸载函数
static int __init my_init(void)
{
// TODO
return 0;
}
static void __exit my_exit(void)
{
// TODO
}
module_init(my_init);
module_exit(my_exit);
在字符设备驱动模块加载函数中应该实现设备号的申请和cdev的注册,而在卸载函数中应实现设备号的释放和cdev的注销。
模板
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#define DEV_CNT 1
#define DEV_NAME "xxx" /* 设备名 */
struct xxx_dev_t {
dev_t devid;
struct cdev cdev;
struct class* class;
struct device* device;
int major;
int minor;
};
static struct xxx_dev_t xxx_dev;
static int xxx_open(struct inode* indoe, struct file* filp)
{
filp->private_data = &xxx_dev;
return 0;
}
static ssize_t xxx_read(struct file* filp, char __user* buf, size_t cnt, loff_t* offt)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t xxx_write(struct file* filp, const char __user* buf, size_t cnt, loff_t* offt)
{
return 0;
}
static int xxx_release(struct inode* inode, struct file* filp)
{
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations xxx_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = xxx_open,
.read = xxx_read,
.write = xxx_write,
.release = xxx_release,
};
static int __init xxx_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
/* 1、注册字符设备驱动 */
/* 1.1 创建设备号 */
if (xxx_dev.major) {
xxx_dev.devid = MKDEV(xxx_dev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(xxx_dev.devid, DEV_CNT, DEV_NAME);
} else {
alloc_chrdev_region(&xxx_dev.devid, 0, DEV_CNT, DEV_NAME);
xxx_dev.major = MAJOR(xxx_dev.devid);
xxx_dev.minor = MINOR(xxx_dev.devid);
}
printk("xxx chr dev major = %d,minor = %d\n", xxx_dev.major, xxx_dev.minor);
/* 1.2 初始化cdev */
xxx_dev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&xxx_dev.cdev, &xxx_fops);
/* 1.3 添加一个cdev */
cdev_add(&xxx_dev.cdev, xxx_dev.devid, DEV_CNT);
/* 1.4 创建类 */
xxx_dev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, DEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(xxx_dev.class)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(xxx_dev.class);
printk("%s: class create failed, ret:%d\n", __func__, ret);
goto class_err;
}
/* 1.5 创建设备 */
xxx_dev.device = device_create(xxx_dev.class, NULL, xxx_dev.devid, NULL, DEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(xxx_dev.device)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(xxx_dev.device);
printk("%s: device create failed, ret:%d\n", __func__, ret);
goto device_err;
}
printk("%s: exit()\n", __func__);
return 0;
device_err:
class_destroy(xxx_dev.class);
class_err:
cdev_del(&xxx_dev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(xxx_dev.devid, DEV_CNT);
return ret;
}
static void __exit xxx_exit(void)
{
/* 注销字符设备驱动 */
device_destroy(xxx_dev.class, xxx_dev.devid);
class_destroy(xxx_dev.class);
cdev_del(&xxx_dev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(xxx_dev.devid, DEV_CNT);
}
module_init(xxx_init);
module_exit(xxx_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("author");
上述例程中额外加了class_create和device_create这两个函数,用于在/dev目录下生成DEV_NAME设备文件.如果不加这两个函数就不会在/dev目录下自动生成DEV_NAME文件。